Capital Gains Tax Deferral
About Capital Gains Taxes
Discover the capital gains tax deferral benefits with a DST at Freedom Bridge Capital. Our Deferred Sales Trust can help investors defer capital gains taxes on the sale of their business, practice, or real estate. Traditionally, you would sell your asset and then have to pay 20-35% in capital gains tax. Capital gains refers to the overall profit you made on your asset. If you made a $2 million dollar profit, over one-fifth of that would be paid in capital gains taxes. The Deferred Sales Trust is a tax deferral strategy that can help owners defer paying capital gains tax on the proceeds of their sale.
What Does “Capital Gain” Mean?
The term “capital gain” refers to the profit made when you sell your asset. Another way to think of it is to calculate the difference between the amount you sold your asset for and the amount you bought it for. For example, if you bought your property for $500,000 and sold it for $3 million, your capital gains would be $2.5 million.
HOW ARE CAPITAL GAINS TAXED?
Capital gains are taxed at varying rates by the IRS. Capital gains are broken down into two categories: long-term capital gains and short-term capital gains. Your capital gains tax rate will vary by the profit, filing status, and length of investment. We’ve laid out the different capital gains tax rates below.
$3 Million (Amount You Sold For) - $500,000 (Amount You Bought For) = $2.5 Million (Capital Gains)
Long-Term Capital Gains
You owe long-term capital gains taxes on assets that you’ve owned for more than one year. The majority of investors hold assets like businesses and real estate for longer than a year because they can make more on their investment over time. Long-term capital gains tax rates are, on average, lower than short-term capital gains rates. This is because the U.S. tax system tends to benefit longer-term investments. Below are the current tax rates for long-term capital gains.
Short-Term Capital Gains
You owe short-term capital gains on the sale of assets you’ve owned for one year or less. Some investors choose to buy companies or real estate and flip them within a year for quicker gains. Typically, short-term capital gains tax rates are higher than long-term rates because the tax system tends to favor longer-term investments. Short-term capital gains tax rates are the same as your ordinary income tax brackets. Below are the current tax rates for short-term capital gains.
Net Investment Income Tax
Also referred to as the “Obamacare Tax,” the Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT) was put in place by President Barack Obama in January 2013. NIIT applies an additional 3.8% tax on individuals, trusts, and estates whose net investment income exceeds the below thresholds. If you sell your business or property, you may be liable to pay the NIIT tax in addition to the standard capital gains tax rates.
CALCULATE YOUR CAPITAL GAINS TAX TODAY
Contact us today for a calculation of your capital gains tax.
CAPITAL GAINS TAX EXAMPLE
Let’s say a business owner is ready to transition to retirement. He or she wants to sell their business and live off the proceeds of the sale.
DEFERRING CAPITAL GAINS TAX

USING DEFERRED SALES TRUST TO SAVE

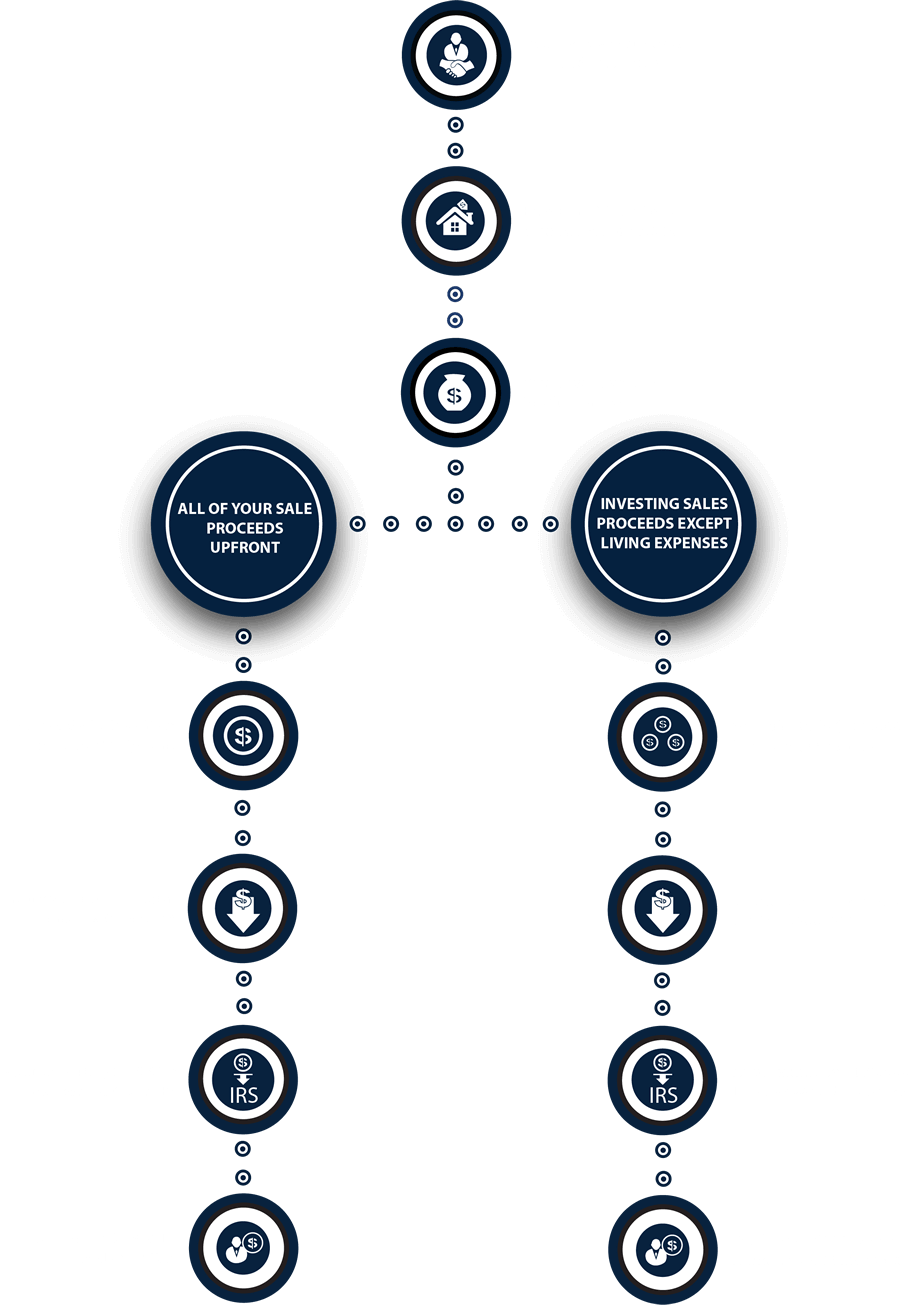
WHAT IF I NEED SOME OF THE SALES PROCEEDS? DO I STILL PAY CAPITAL GAINS TAX?
Even if you need to take out a portion of your proceeds, the Deferred Sales Trust can help you reduce capital gains tax. If you cash-out a portion of your profit, you only pay capital gains tax on that portion specifically. Let’s say you take $500,000 of your $7.5 million profit and would like the trust to invest the rest – you will only pay capital gains tax on the $500,000.*
USING DST TO EASE TAX BURDEN
HOW LONG DOES MY CAPITAL GAINS TAX DEFERRAL LAST?
When you sell your business or property to the Deferred Sales Trust, you can defer your capital gains tax as long as the trust is investing the proceeds from your sale. As long as you do not withdraw any principle, you will not have to pay capital gains tax.
Many clients choose to defer their capital gains taxes electing for the trust to invest the entire principal. This allows them to receive monthly payments for the interest accrued on the trust’s investments. Your interest is subject to standard income tax, but not capital gains tax. This strategy allows for a steady income stream for you and your estate.